“SEL is the foundation for developing a healthy and thoughtful generation of individuals. If we want children to thrive, we need to meet their social and emotional needs first.”
What You’ll Learn
- What is social-emotional learning (SEL)?
- Why is SEL important?
- What does SEL look like?
Over the past few years, the term “social-emotional learning” became a buzzword in the field of education, and unfortunately, there is often a lack of understanding about what this term means. Social-emotional learning (SEL) is an integral part of human development and I’m here to explain why. (Hint: it’s more than teaching children about their feelings and is just as important as teaching them about numeracy or literacy skills).
Social-Emotional Learning
Social-emotional learning (SEL) inspires learning and growth—it is the process through which all human beings acquire the knowledge, skills, and attitudes to become a thriving individual. These skills include managing difficult emotions, developing a healthy identity, making decisions, handling stress, setting goals, and maintaining supportive relationships. SEL is the foundation for developing a healthy and thoughtful generation of individuals.
5 Areas of Social and Emotional Competence
The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) is a leader in the field of SEL instruction. CASEL identifies five broad and interrelated areas of competence of SEL:
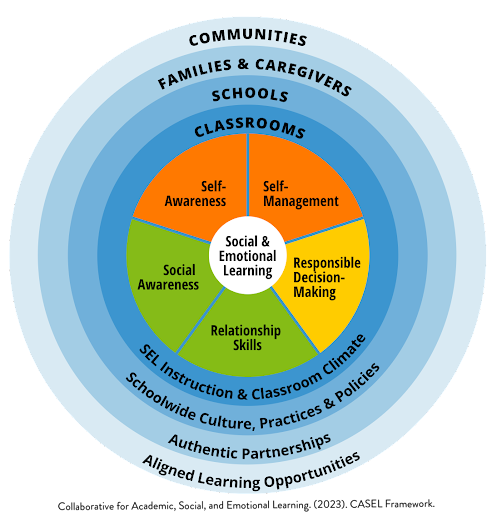
- Self-awareness: The ability to understand one’s own emotions, thoughts, and values and how they influence behavior across contexts.
- Developing a healthy sense of identity
- Identifying one’s emotions
- Recognizing one’s strengths and needs
- Developing a growth mindset
- Self-management: The ability to manage one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors effectively in different situations and to achieve goals and aspirations.
- Managing one’s emotions
- Feeling empowered to make choices and take action
- Exhibiting self-control
- Setting personal and collective goals
- Social awareness: The ability to understand the perspectives of and empathize with others, including those from diverse backgrounds, cultures, and contexts.
- Taking others’ perspectives
- Demonstrating empathy
- Showing concern for the feelings of others
- Understanding and expressing gratitude
- Relationship skills: The ability to establish and maintain healthy and supportive relationships and to effectively navigate settings with diverse individuals and groups.
- Communicating effectively
- Resolving conflicts in collaboration with others
- Seeking or offering support and help when needed
- Standing up for the rights of others
- Responsible decision-making: The ability to make caring and constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions across diverse situations.
- Demonstrating curiosity and open-mindedness
- Considering the consequences of one’s actions
- Identifying solutions for personal and social problems
- Reflecting on one’s personal impact
These core competencies underscore one’s ability to be available to learn and help to create communities that are caring and just. If we want children to thrive, we need to meet their social and emotional needs first.
Social-Emotional Learning is Effective
Social-emotional learning is an opportunity to ensure long-term benefits for all children. Research continues to demonstrate that SEL can prevent problems and promote positive outcomes. Social-emotional learning:
- Improves academic performance and achievement
- Develops skills that promote future readiness
- Creates safe and supportive learning environments
- Advances educational equity
- Cultivates protective factors to buffer against mental health risks
- Helps reduce poverty and improves economic mobility
Social-Emotional Learning in Practice
Social-emotional learning does not occur naturally over the course of a child’s development, but these skills can be taught and learned across one’s lifespan. In educational settings, SEL competencies are integrated into students’ daily learning experiences and taught through explicit instruction. Explicit instruction often includes lessons on how to identify and label feelings, build emotional vocabulary, consider other people’s perspectives and experiences, and brainstorm solutions to problems. Consistent and differentiated instruction is essential for the development of a student’s social-emotional skills.
At home, parents and caregivers can also reinforce SEL competencies through modeling these skills when interacting with their child and with others.
Empowering Takeaways
- SEL is an integral part of human development and is the foundation for a healthy and thoughtful generation of individuals
- There are five core competencies of SEL: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision making
- SEL can prevent problems and promote positive, life-long benefits
Be vibrant and keep thriving!
This article was last reviewed or updated on November 17, 2023.
References
Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning. (2023). Transformative SEL. https://casel.org/fundamentals-of-sel/how-does-sel-support-educational-equity-and-excellence/transformative-sel/
Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning. (2023). What is the CASEL framework? https://casel.org/fundamentals-of-sel/what-is-the-casel-framework/#social-emotional-learning
Duffell, J. C., Weissberg, R. P., Williams, A., Eaton, P. D., Segneri, M., Carstarphen, M. J., Matheny, R. K., Amador, A., Koch, R., & Kranzler, D. (n.d.). How social-emotional learning helps children succeed in school, the workplace, and life. Committee for Children. https://www.cfchildren.org/wp-content/uploads/mission-vision/what-is-sel/docs/sel-e-book.pdf
Gregory, A., & Fergus, E. (2017). Social and emotional learning and equity in school discipline. The Future of Children, 27(1), 117-137.
Jones, S. M., & Doolittle, E. J. (2017). Social and emotional learning: Introducing the issue. The Future of Children, 27(1), 3-11. https://www.jstor.org/stable/44219018
Massachusetts Department of Elementary and Secondary Education. (2023). Social and emotional learning in Massachusetts. https://www.doe.mass.edu/sfs/sel/?section=all#topics
Posamentier, J. (2020, September 1). Supporting racial equity with culturally responsive pedagogy and SEL. Committee for Children. https://www.cfchildren.org/blog/2020/09/supporting-racial-equity-with-culturally-responsive-pedagogy-and-sel/?_gl=1*1ke2y67*_ga*MTAzMzg0MjY0LjE3MDAxOTM0MjE.*_ga_RCFK1P818T*MTcwMDE5MzQyMS4xLjAuMTcwMDE5MzQyMS42MC4wLjA.
Souza, J. (2023, June 2). What is social and emotional learning. Child Mind Institute. https://childmind.org/article/what-is-social-and-emotional-learning/?utm_medium=email&utm_source=newsletter&utm_campaign=pub_ed_nl_2023-03-21&utm_content=what-is-social-and-emotional-learning
Tate, E. (Host). (2019, May 7). Why social-emotional learning is suddenly in the spotlight [Audio podcast episode]. In EdSurge On Air Podcast. EdSurge. https://soundcloud.com/edsurge/why-social-emotional-learning-is-suddenly-in-the-spotlight



